Exchange 2010: What are your Admins doing?
A new feature of Exchange Server 2010 allows you to keep an eye on all the activities of administrators performed through Exchange Management Shell, Exchange Management Console, or by Exchange Web management interface and it is called Administrator Audit Logging.
Isn’t it cool to comply with regulatory requirements and requests for discovery? ![]()
Let’s see how to configure it in Exchange 2010 environment. You need to have Organization Management role or RBAC to enable and configure it.
1. Enable Administrator Audit Logging
We can enable it with below cmdlet.
Set-AdminAuditLogConfig -AdminAuditLogEnabled $True
2. Configure the Auditing Mailbox
We need to specify the auditing mailbox where auditing log entries, for each and every cmdlets (except starting with Get*) or for specified cmdlets and/or parameters enabled for auditing, will be stored for review. Run below cmdlet to specify the mailbox for logs.
Set-AdminAuditLogConfig -AdminAuditLogMailbox AdminAuditLogs@ExchangeShare.net
- I recommend to create a Shared mailbox for Auditing Mailbox.
- Restrict the auditing mailbox tightly to access by certain group of administrator because it contains sensitive information like values of all parameters (except Password) of the cmdlets ran by users or administrators.
- Monitor it regularly or configure MRM to purge old entries otherwise when it becomes full new entries will not be logged.
3. Configure cmdlets and parameters for Auditing
By default when you enable Admin Audit Logging as per step-1, all cmdlets and parameters (except cmdlet starts with Get*) are configured for auditing. But if you want to audit specific cmdlets or parameters, it can be configured with below methods.
3.1. Configure list of cmdlets to be audited.
You can specify cmdlets, cmdlet entries with wild card search or both in AdminAuditLogCmdlets parameter of Set-AdminAuditLogConfig.
Example: Set-AdminAuditLogConfig -AdminAuditLogCmdlets New-Mailbox, *TransportRule, *Management, Set-Transport*
3.2. Configure list of Parameters to be audited.
Similarly like cmdlets configuration you can specify parameters, parameter entries with wild card search or both in AdminAuditLogParameters parameter of Set-AdminAuditLogConfig
Example: Set-AdminAuditLogConfig -AdminAuditLogParameters Database, *Address*, Custom*, *Region
AdminAuditLogCmdlets and AdminAuditLogParameters are multivalued properties so if you want to add or remove any cmdlet or parameter in the list at later stage, you need to follow Modifying Multivalued Properties article otherwise it will replace/remove previous entries.
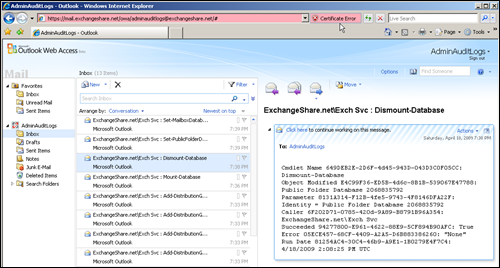
4. Review Audit Logs
You can open Auditing mailbox in Outlook or OWA to review log entries which are stored as email messages.
Example:
Subject Format: User account who ran the cmdlet: Cmdlet name
Body Message: It contains cmdlet name, object modified, parameter, caller, succeeded , error and run time of cmdlet.

[…] by Amit Tank on 2009/04/18 Exchange 2010: What are your Admins doing? – Amit Tank (Me […]
Exchange Daily Article: Apr 18, 2009 « Exchange Server Readings
April 20, 2009 at 9:42 am
[…] Amit has a great review of Audit Logging […]
Exchange Server 2010 Features « Messaging….. Technology…… Life…..
April 21, 2009 at 8:40 pm
It’s AdminAuditLogEnabled and not AdminAuditLoggingEnabled 🙂
Christian
May 15, 2009 at 8:26 pm
Ahh, thanks for identifying it Christian. I just corrected it.
Amit Tank
May 15, 2009 at 9:02 pm
[…] Enhanced audit logging possible using shell. Any modifications done in Exchange organization configuration or any other exchange objects using either ESM,web management interface or shell will be logged & can be tracked.Check out the detailed information here […]
Exchange 2010 beta:Some new features to look forward to « Kiran’s Blog
May 28, 2009 at 3:57 am